Student Loans 101: Federal vs. Private Loans Explained
Navigating the world of student loans can be overwhelming, especially when trying to understand the differences between federal and private loans. Choosing the right type of loan is crucial for managing your debt effectively and ensuring financial stability after graduation. In this guide, we’ll break down the key distinctions between federal and private student loans, helping you make an informed decision.
What Are Federal Student Loans?
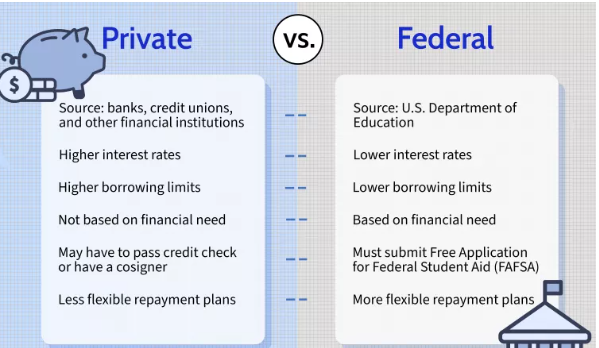
Federal student loans are loans issued by the U.S. Department of Education to help students and parents cover the cost of higher education. These loans typically come with lower interest rates and borrower-friendly repayment options.
Types of Federal Student Loans:
- Direct Subsidized Loans: Available to undergraduate students with financial need. The government pays the interest while the student is in school and during deferment periods.
- Direct Unsubsidized Loans: Available to undergraduate, graduate, and professional students, regardless of financial need. Interest accrues from the moment the loan is disbursed.
- Direct PLUS Loans: Offered to graduate students and parents of dependent undergraduates. A credit check is required, and interest rates are typically higher than other federal loans.
- Direct Consolidation Loans: Allow borrowers to combine multiple federal loans into one loan with a single monthly payment.
Pros of Federal Student Loan:
- Lower, fixed interest rates
- Income-driven repayment plans
- Loan forgiveness options (e.g., Public Service Loan Forgiveness)
- Deferment and forbearance options in cases of financial hardship
- No credit check is required (except for PLUS loans)
Cons of Federal Student Loans:
- Borrowing limits may not cover the full cost of education
- Interest still accrues on unsubsidized loans
- Limited flexibility in choosing a lender
What Are Private Student Loans?
Private student loans are issued by banks, credit unions, and other private lenders. These loans typically have higher interest rates and fewer borrower protections than federal loans.
Key Features of Private Student Loans:
- Interest rates can be fixed or variable
- Loan amounts may be higher to cover full tuition costs
- Often require a credit check or a cosigner
- Repayment terms vary by lender
Pros of Private Student Loans:
- Can cover the full cost of attendance, including living expenses
- May offer competitive rates for borrowers with excellent credit
- More options for loan customization
Cons of Private Student Loan:
- Higher interest rates compared to federal loans
- No income-driven repayment plans
- No federal loan forgiveness programs
- Fewer protections for deferment and forbearance
Which Loan Should You Choose?
For most students, federal student loan should be the first choice due to their lower interest rates, flexible repayment plans, and forgiveness options. However, if you’ve maxed out federal loan options and still need additional funds, private loans can help fill the gap. When considering private loans, be sure to shop around for the best rates and terms.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the differences between federal and private student loans is essential for making the right financial decision. If possible, maximize federal loan options before considering private loans, and always evaluate repayment options to ensure financial security in the future. Smart borrowing today can lead to a more stable financial future after graduation!