How Interest Rates on Loans Work and What Affects Them
Interest rates play a crucial role in borrowing money, whether for a home, a car, or a personal expense. Understanding how these rates work and the factors that influence them can help you make informed financial decisions. In this post, we’ll break down the basics of loan interest rates and explore the key factors that affect them.
What is an Interest Rate?
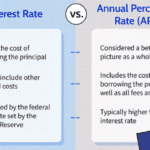
An interest rate is the cost of borrowing money, expressed as a percentage of the loan amount. Lenders charge interest to compensate for the risk they take in lending money. The higher the interest rate, the more you’ll pay over time.
There are two main types of interest rates:
- Fixed Interest Rate: This rate remains constant throughout the loan term, ensuring predictable monthly payments.
- Variable Interest Rate: This rate fluctuates based on market conditions, meaning your payments could increase or decrease over time.
What Affects Interest Rates on Loans?
Several factors influence the interest rate you receive on a loan. Here are some of the most significant ones:
1. Credit Score
Your credit score is one of the most critical factors in determining your interest rate. Lenders use it to assess your creditworthiness. A higher credit score generally leads to lower interest rates, while a lower score results in higher rates due to the increased risk for the lender.
2. Loan Type
Different types of loans have different interest rate structures. For example:
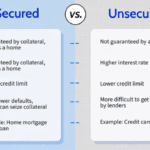
- Mortgage loans often have lower interest rates due to their long-term nature and secured status.
- Personal loans typically have higher rates because they are unsecured, meaning no collateral backs them.
- Auto loans have moderate rates since the vehicle serves as collateral.
3. Loan Term
The length of the loan also affects the interest rate. Shorter loan terms usually have lower rates but higher monthly payments, while longer terms may have higher rates but lower monthly payments.
4. Market Conditions
Economic factors, such as inflation and central bank policies, influence interest rates. When inflation rises, central banks may increase rates to slow borrowing and spending. Conversely, during economic downturns, they may lower rates to encourage borrowing and investment.
5. Lender Policies
Each lender sets its own interest rates based on risk assessments, competition, and internal policies. Shopping around and comparing rates from different lenders can help you find the best deal.
6. Down Payment & Loan-to-Value Ratio
For secured loans like mortgages or auto loans, a higher down payment or lower loan-to-value (LTV) ratio can result in lower interest rates. This is because the lender assumes less risk when you have more equity in the asset.
How to Get the Best Interest Rate on a Loan
If you’re looking to secure a loan at the lowest possible interest rate, consider these tips:
- Improve Your Credit Score: Pay bills on time, reduce outstanding debt, and check your credit report for errors.
- Compare Lenders: Don’t settle for the first offer—shop around to find the best rate.
- Consider a Shorter Loan Term: If you can afford higher monthly payments, opting for a shorter loan term can save you money in interest.
- Make a Larger Down Payment: If possible, put more money down to lower your interest rate.
- Monitor Market Trends: If interest rates are expected to decrease, you may want to wait before borrowing.
Final Thoughts
Understanding how loan interest rates work and what affects them is crucial for making sound financial decisions. By knowing the factors that influence rates and taking proactive steps to secure a lower rate, you can save money and manage your debt more effectively. Whether you’re applying for a mortgage, auto loan, or personal loan, being informed can help you navigate the borrowing process with confidence.