Forex vs. Stock Market: Which One is Better for You?
When it comes to investing and trading, two of the most popular markets are Forex (foreign exchange) and the stock market. Both offer opportunities to grow wealth, but they cater to different types of traders and investors. So, which one is better for you? Let’s break down the key differences to help you decide.
1. Understanding Forex Market
- Forex Market: The Forex market involves trading currencies in pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/JPY). It is the largest and most liquid market globally, with a daily trading volume exceeding $7 trillion.
- Market: The stock market allows investors to buy shares in publicly traded companies. Investors can own a piece of a company and benefit from price appreciation, dividends, and long-term growth.
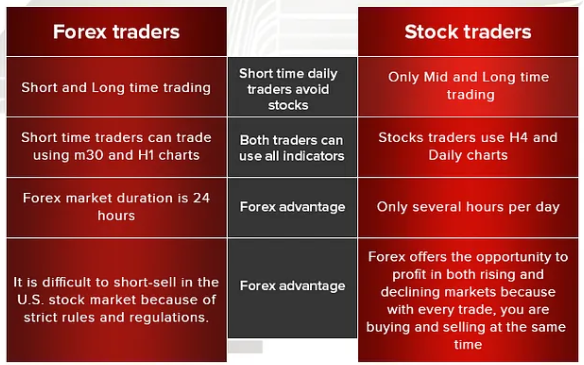
2. Trading Hours and Liquidity
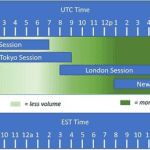
- Forex: Open 24 hours a day, five days a week, due to its global nature. It is highly liquid, meaning traders can enter and exit positions with ease.
- Market: Typically operates during standard business hours of the stock exchange (e.g., NYSE and NASDAQ operate from 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM EST). Liquidity varies based on the stock’s popularity and volume.
3. Market Volatility and Risk
- Forex: The Forex market is highly volatile, influenced by economic events, interest rates, and geopolitical factors. High volatility can lead to large gains but also significant losses.
- Market: Individual stocks can be volatile, but overall, the stock market tends to be less volatile than Forex. Diversification through ETFs and index funds can further reduce risk.
4. Leverage and Capital Requirements
- Forex: Forex brokers offer high leverage (often up to 50:1 or more), allowing traders to control larger positions with less capital. While this can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of substantial losses.
- Market: Leverage in the stock market is lower, typically up to 2:1 for retail investors. This makes stock trading less risky compared to Forex trading when it comes to margin use.
5. Investment vs. Trading
- Forex: Primarily suited for short-term trading strategies, including day trading and scalping. It is not ideal for long-term investing.
- Market: Suitable for both short-term trading and long-term investing. Investors can build wealth over time through dividends, stock appreciation, and reinvestment.
6. Fundamental and Technical Analysis
- Forex: Traders rely heavily on technical analysis, economic indicators, and central bank policies.
- Market: Investors analyze financial statements, earnings reports, industry trends, and company fundamentals, along with technical analysis.
7. Tax Implications
- Forex: Taxation on Forex trading varies by country and can be complex. Some countries have lower tax rates for Forex traders.
- Market: Stocks are subject to capital gains tax, dividend tax, and other regulations depending on the country.
Which One is Right for You?
- Choose Forex if you prefer fast-paced trading, higher leverage, and global economic trends.
- Choose the Market if you seek long-term growth, lower volatility, and company ownership benefits.