Fixed vs. Variable Interest Rates: Which is Right for You?
When taking out a loan or mortgage, one of the most important decisions you’ll face is whether to choose a fixed or variable interest rate. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice depends on your financial situation, risk tolerance, and market conditions. In this post, we’ll break down the differences between fixed and variable interest rates and help you determine which might be best for you.
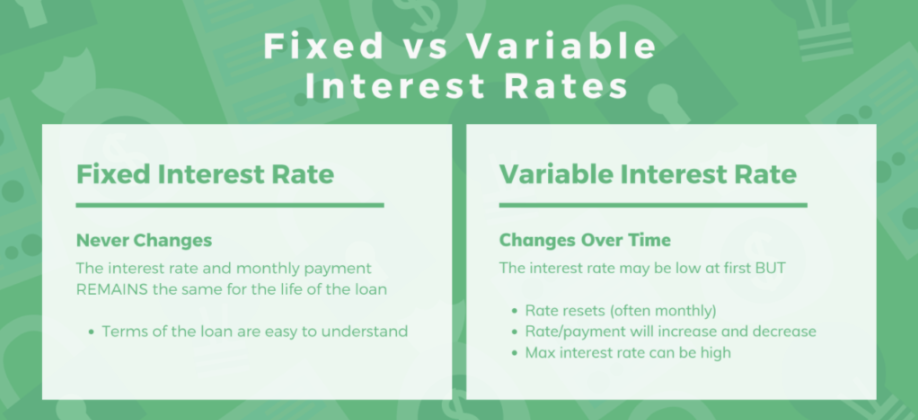
What is a Fixed Interest Rate?
A fixed interest rate remains the same throughout the life of the loan. This means that your monthly payments stay consistent, making it easier to budget and plan for the future. Fixed rates are commonly used in mortgages, personal loans, and auto loans.
Pros of Fixed Interest Rates:
- Predictability: Your monthly payment remains the same, which simplifies budgeting.
- Protection from Rate Hikes: If interest rates rise in the future, your rate stays locked in.
- Stability: Ideal for those who prefer long-term financial certainty.
Cons of Fixed Interest Rates:
- Higher Initial Rate: Fixed rates are generally higher than the initial rate on a variable loan.
- Less Flexibility: If interest rates drop, you won’t benefit unless you refinance.
What is a Variable Interest Rate?
A variable (or adjustable) interest rate fluctuates over time based on a benchmark interest rate, such as the prime rate or LIBOR. This means your payments can increase or decrease, depending on market conditions.
Pros of Variable Interest Rates:
- Lower Initial Rates: Typically, variable rates start lower than fixed rates, making them attractive for short-term savings.
- Potential for Savings: If interest rates decline, you could end up paying less over time.
- More Flexibility: Some variable-rate loans allow for extra payments without penalties.
Cons of Variable Interest Rates:
- Uncertainty: Your monthly payments could rise, making budgeting more difficult.
- Potential for Higher Costs: If interest rates increase significantly, you may end up paying more than with a fixed-rate loan.
- Market Dependency: Your loan cost depends on economic conditions beyond your control.
Which Option Is Right for You?
The best choice depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance:
- Choose a fixed interest rate if:
- You prefer stable and predictable payments.
- You plan to keep the loan for a long time.
- You want to avoid the risk of rising interest rates.
- Choose a variable interest rate if:
- You can handle potential payment fluctuations.
- You believe interest rates will remain low or decrease.
- You plan to pay off the loan quickly or refinance before potential rate hikes.
Final Thoughts
Both fixed and variable interest rates have their merits, and the right choice depends on your financial situation and comfort level with risk. If stability is your priority, a fixed rate may be your best bet. If you’re willing to take on some risk for potential savings, a variable rate could work in your favor. Before making a decision, consider speaking with a financial advisor to assess your options and choose the loan structure that best aligns with your financial goals.